Durable Medical Equipment (DME) – a medically necessary device that you can use over and over – is prescribed to injured worker patients who have an injury or disability. Commonly prescribed DME items in workers’ compensation include Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) devices, thermal compression devices, and reusable electrodes.
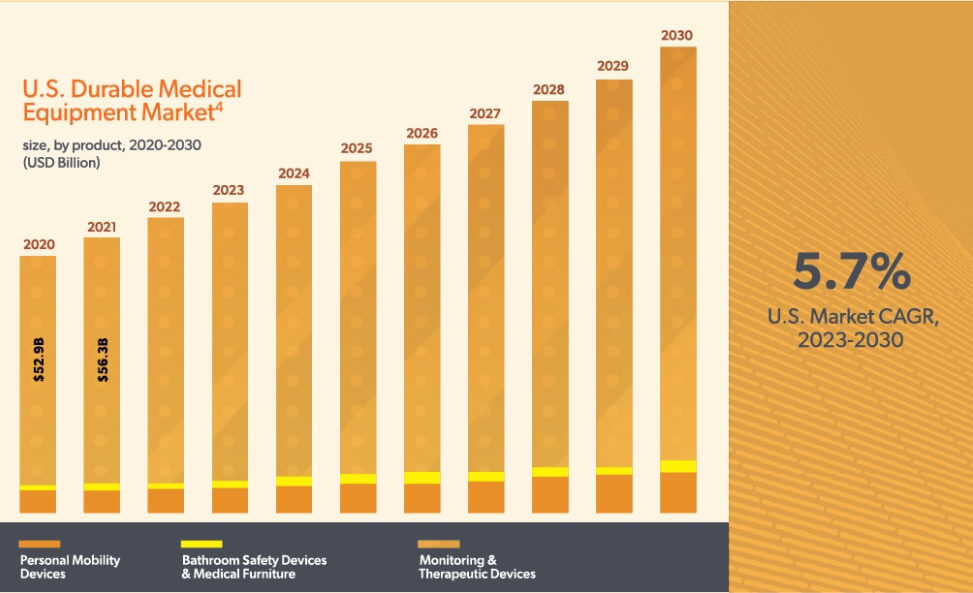
The market for DME is increasing due to rising product demand. This demand is driven by increasing penetration of home healthcare services, high occurrence of chronic conditions, and the growing elderly population.1 The DME market was valued at $59.7 billion in 2022, with an expected compound annual growth rate of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030.2 In workers’ compensation specifically, DME, prosthetics, orthotics, and supplies comprise 4 to 13% of medical costs, depending on the state.3
While a common and expected component of many work-related injuries, certain DME trends bear watching in workers’ comp claims due to cost and clinical considerations. Claims adjusters should be aware that sometimes medical evidence for these trendy devices is limited or absent. In these cases, there are often more conventional, appropriate, and cost-effective treatment modalities available.
DME is defined as equipment that meets these criteria:

These portable, self-contained units provide hot and cold therapies, often combined with compression, to treat pain, inflammation, swelling, and circulation in the extremities. Thermal Compression Therapy is considered investigational, as there is no significant clinical evidence to support that it provides greater results than standard cryotherapy (ice packs or reusable gel hot/cold packs).

These electrotherapy devices are designed to stimulate therapeutic muscle and nerve activity for muscle relaxation and longer lasting pain relief. H-Wave is considered investigational based on a lack of clinical evidence supporting a significant reduction in pain, edema, increased function, or range of motion. Instead, patients should try TENS devices, physical therapy, home exercises, and medications.

This is an electrical modality used for the treatment of pain, edema, and soft tissue injuries. It is theorized that IFC penetrates deeper into the soft tissue than traditional TENS therapy, providing improved pain control. However, IFC is widely considered investigational based on a lack of clinical evidence. Instead, patients should try conservative measures such as repositioning, heat/ice, and medications.

These are short surges of electromagnetic energy that can be used to stimulate and heal cells. PEMF is prescribed for the treatment of pain, swelling, inflammation, and wounds. It works by penetrating deep soft tissue to enhance the anti-inflammatory response of the body. However, there is insufficient clinical evidence showing that PEMF is effective.

For more information on the above DME trends, check out our Clinical Minute video series with Tate Rice, DPT, PT, MBA.
Healthesystems relies on evidence-based guidelines to support the appropriate use of DME devices in the care of injured workers. Our goal is to keep claims professionals informed of treatment interventions that are proven to be effective and under what circumstances, as well as limit the use of DME devices that are ineffective and often expensive. American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (ACOEM) and ODG are examples of evidence-based guidelines that are focused on safely returning people to their daily lives.